RTKdata Blog
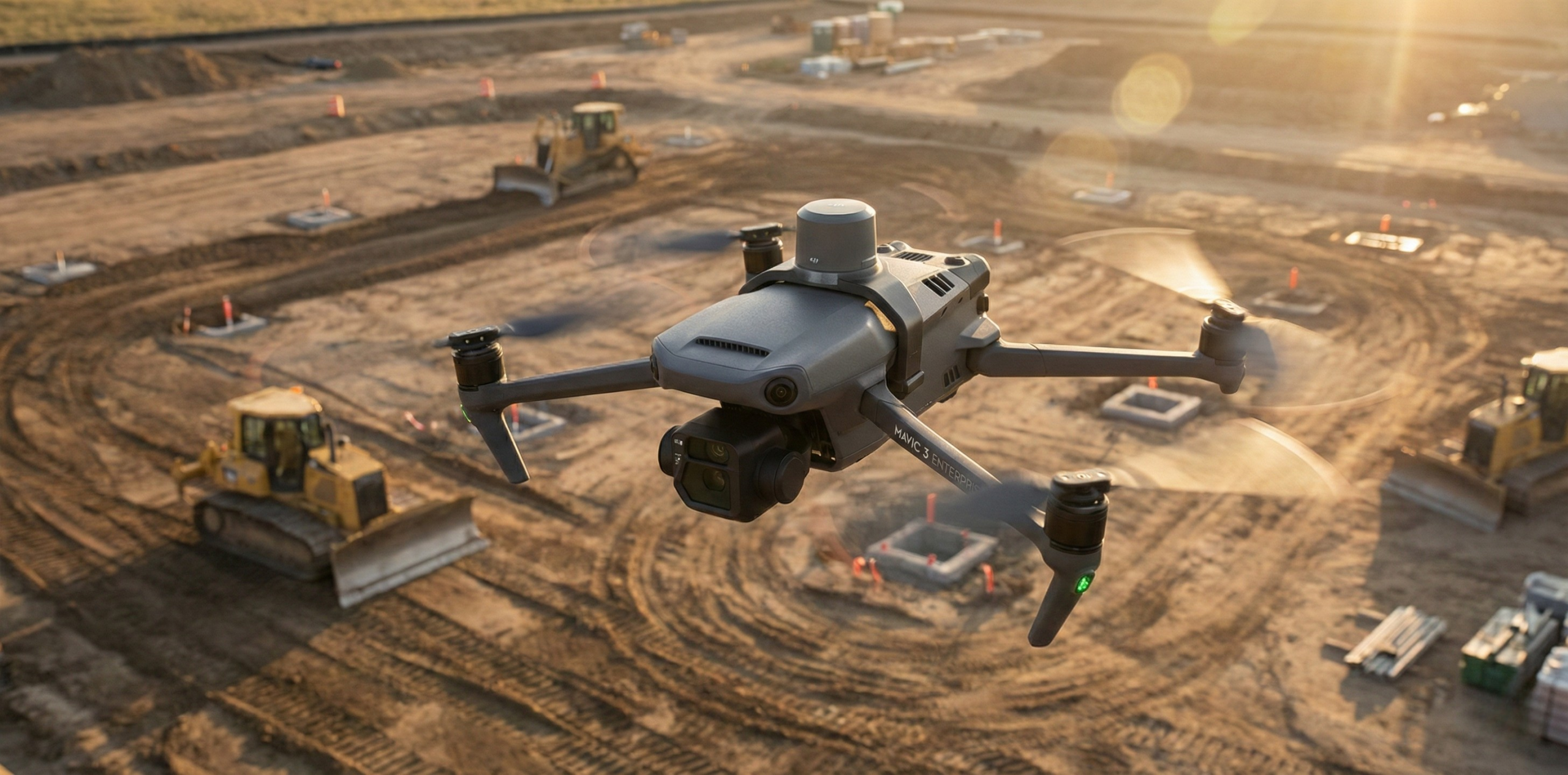

RTK for Drones: Ultimate Precision Explained

How Distance Impacts NTRIP RTK Accuracy and How Network RTK Helps
Baseline distance erodes single-base RTK as atmospheric and other errors stop matching between base and rover. See representative accuracy degradation (≈0.6 cm near the base to ≈3.1 cm at 50 km) and how network RTK models regional errors to keep results steadier.

RTK Multipath: Why Your RTK Fix Drops Out in Cities and Forests
Multipath and signal blockage are common reasons an RTK Fix drops out or looks “good” while being wrong in cities, forests, and mountains. You’ll get a field checklist for mitigation—site choice, antenna placement, and QC signals like Fix/Float transitions and DOP limits.

RTK for Drones: Ultimate Precision Explained
RTK turns a drone’s meter-level GNSS into ~1–3 cm positioning by streaming RTCM corrections via NTRIP over cellular or Wi‑Fi. It covers the key components, why a nearby mountpoint matters, and the basic setup to reach and consistently maintain an RTK Fix.

KPIs That Matter for RTK: Key Metrics for High-Performance GNSS
High-performing RTK is measurable through KPIs like accuracy, availability, integrity, continuity, time‑to‑fix, fix rate, and correction latency/age. The post highlights practical targets and how to track them in logs and dashboards.

Network RTK Comparison: Which System Performs Best?
Network RTK combines multiple reference stations to model distance‑dependent GNSS errors and stream real-time corrections across large regions. It contrasts network vs single‑base setups and shows how station density, uptime, and update rates.

NTRIP connection flow explained
From sourcetable to mountpoint stream, this guide traces the NTRIP connection flow used by rovers and apps. It covers v1 vs v2 handshakes, GGA needs for VRS/NEAR, and resilience: timeouts, backoff, failover, and Age of Corrections.
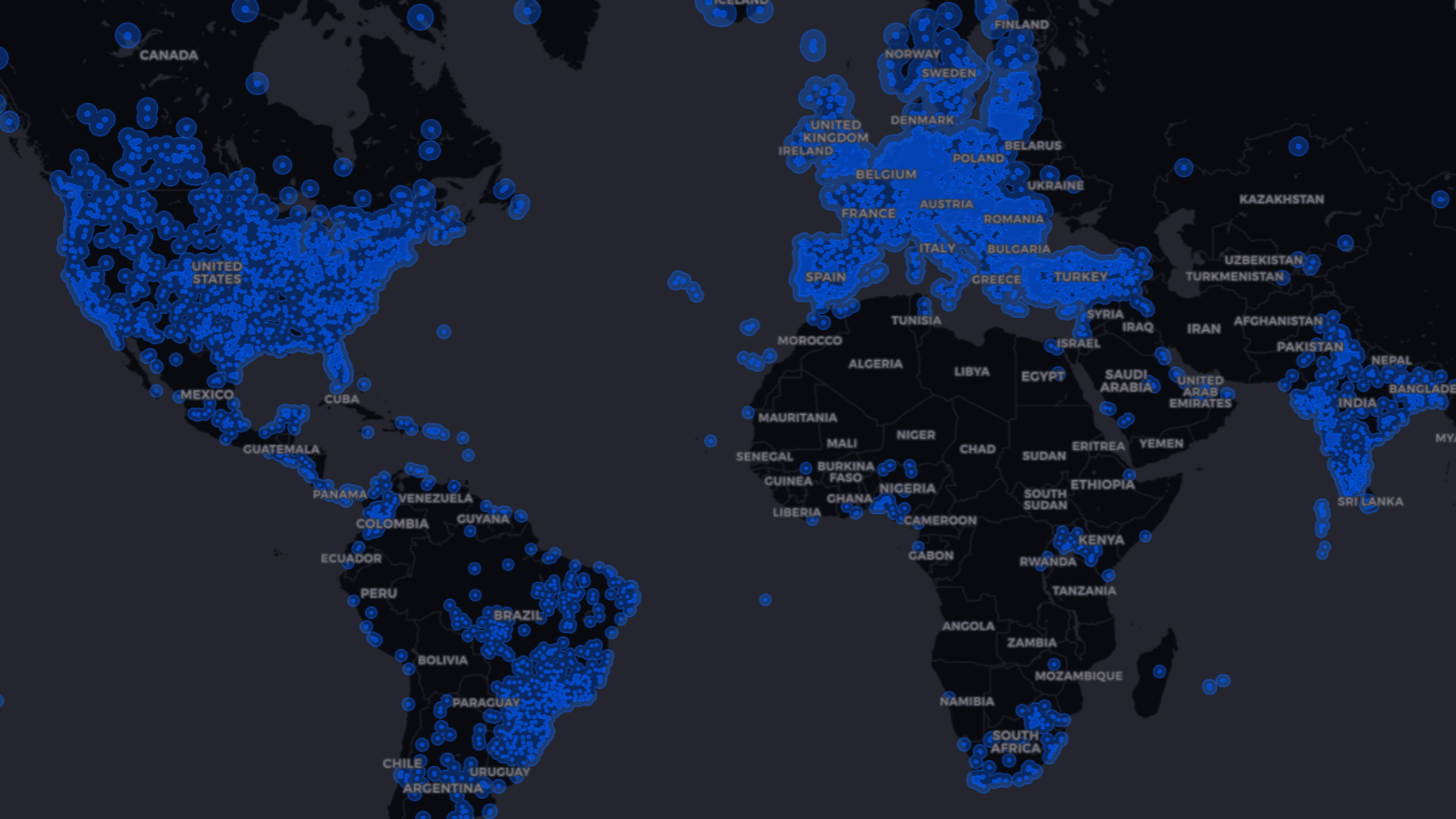
GNSS Corrections Map – Coverage and Accuracy
A GNSS corrections map shows where RTK, PPP/PPP‑RTK, and SBAS are available and what accuracy to expect. Use it to match regional coverage to tolerances and see how corrections shrink 5–10 m standalone errors toward centimeters.
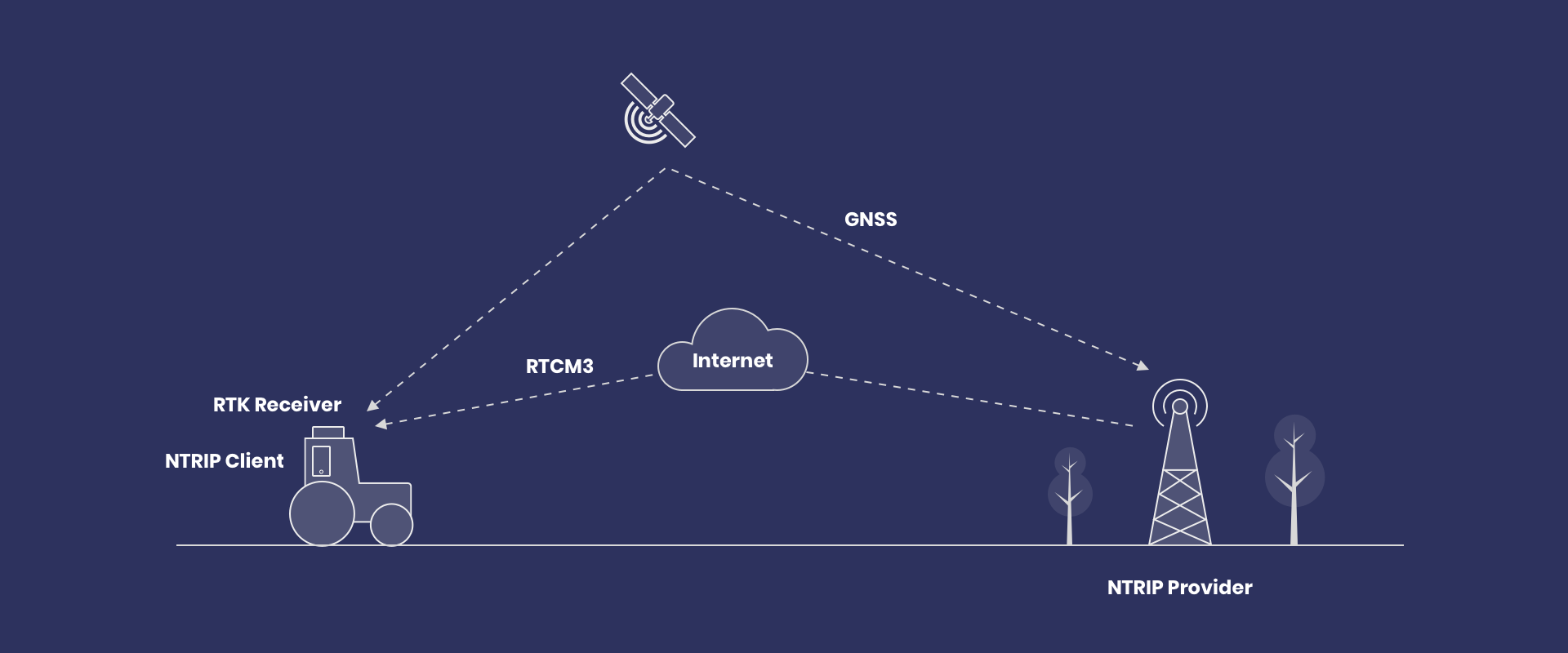
What is NTRIP? RTCM Corrections for GNSS Rovers
NTRIP turns the internet into a real-time pipeline for RTCM corrections, giving GNSS rovers centimeter-level positioning. You’ll learn the core client settings (host, port, credentials, mountpoint) and what to watch—RTK Fix status and correction age.
RTK Troubleshooting Guide: Step-by-step
A practical 7-step checklist helps you stabilize RTK when fixes drop or correction streams lag. It walks through network tests, sky view and hardware checks, NTRIP validation, and monitoring Fix/Float plus correction age (target ~1 s).